The versatility of CO2-cryospraying technology makes it applicable to different types of molecules and excipients.
Lipid-composite systems can be prepared under mild processing conditions starting from mono or biphasic formulated mixtures, containing the dissolved or dispersed APIs. Solid microspheres are instantly formed by cryogenic spraying under the expanding CO2 flow, and collected as micronized powders.
Since expanding CO2 works also as a “cold-drying” agent (“dewatering”), we can directly formulate water-soluble APIs into solid, lipid-based delivery systems.
Case Studies
Celecoxib
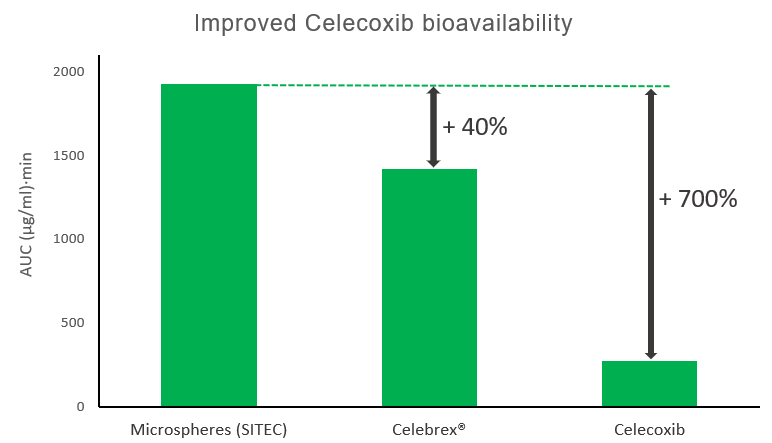
Celecoxib is a BCS class II COX-2i inhibitor used in treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid. Its therapeutic application is limited by cardiovascular toxicity related to high Cmax in plasma, while poor drug solubility leads to scarce and erratic bioavailability. Applying CO2-cryospraying technology, amphiphilic microspheres were developed where:
- Celecoxib was stabilized in the amorphous state within the lipid matrix
- Drug was rapidly dissolved and remained in an absorbable form in the GI tract.
- A 40% increase in oral bioavailability was achieved vs. marketed product, combining a lower Cmax with time-extended high plasma levels.
| Cmax | tmax | t1/2 | C4h | C8h | C24h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | ng/mL | min | min | ng/mL | ng/mL | ng/mL |
| Microspheres (SITEC) | 2861±957 | 60 | 231 | 2536±786 | 1710±263 | 82±13 |
| Celebrex® | 3392±256 | 120 | 223 | 1727±45 | 1097±225 | 50±10 |
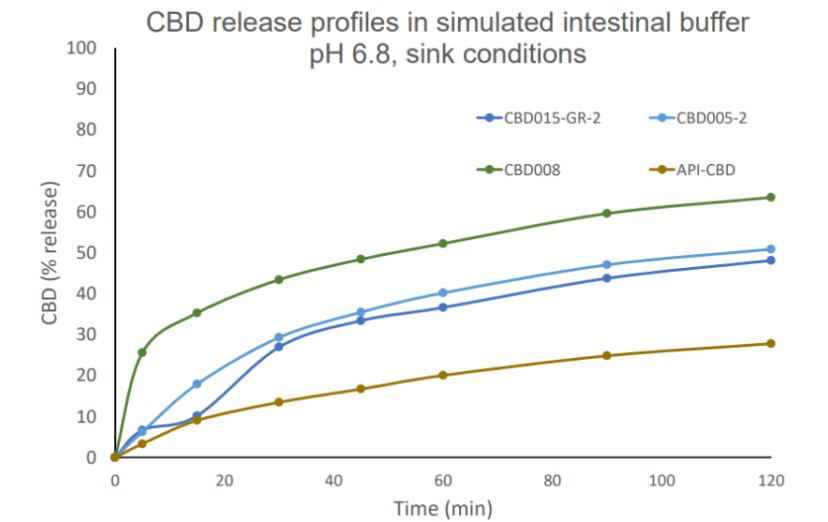
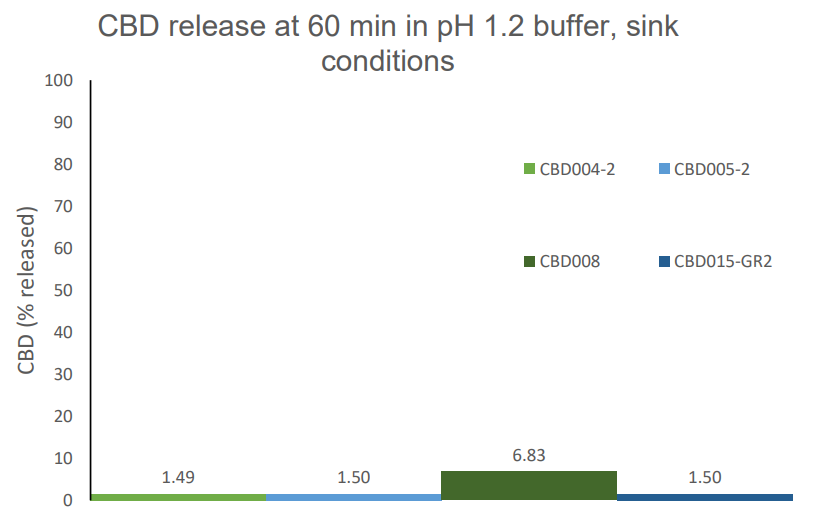
CBD
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychotropic cannabinoid approved for treatment of epileptic syndromes in adults and children. Its use is limited by poor absorption and low oral bioavailability, caused by low aqueous solubility, instability at gastric pH and high 1st pass
effect. CBD is currently marketed as ethanol-oily solution, and administered directly in the patient’s mouth with a graduated syringe for dose adjustment.
A lipid composite microspheres product is a practical alternative for oral administration of CBD:
- Designed as water-dispersible powders with high drug load, gastro-resistant properties and controlled release at intestinal pH,
- Fast dispersion in water or drinks can facilitate administration to patients, without complicated dosing adjustments.
- CBD dose can be personalized for specific therapeutic indications and special patients’ needs (pediatric and geriatric)
Metoclopramide
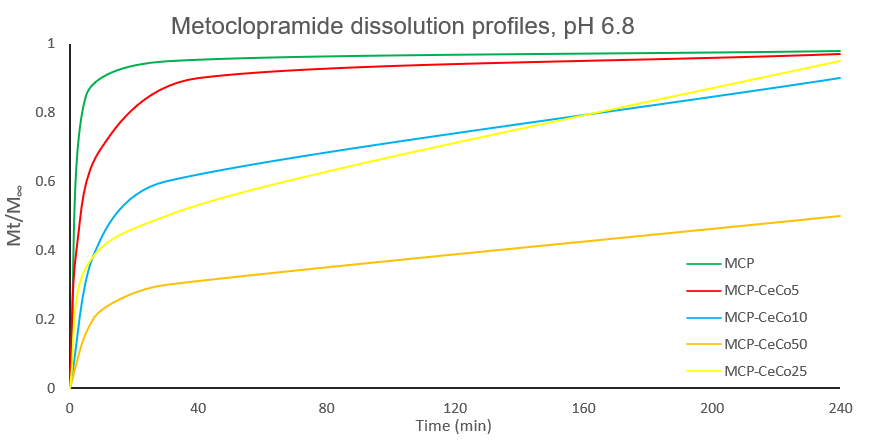
Metoclopramide is an intensely bitter, highly soluble, well absorbed drug used to treat GI disorders and as antiemetic in chemotherapy. Its short half-life necessitates a dosing frequency of 3-4 times/ day to maintain constant drug concentration in plasma. Taste-masked, controlled release formulations are desirable to reduce dosing frequency while maintaining the antiemetic effect. With CO2-cryospraying, it was possible to:
- Encapsulate metoclopramide in lipid microspheres with small average size (20 - 40 µm), limiting contact between drug and taste receptors on the tongue.
- Control and modulate drug release by modifying the excipients composition without significantly changing processing conditions and product particles size.
Pancreatin
Pancreatin is an acid-sensitive, enzymatic complex used to improve digestion in patients who suffer from pancreatic conditions caused by cystic fibrosis or chronic pancreatitis.
Our client needed to develop a new product for pediatric use, meeting specific criteria of high daily dose and restricted excipients selection due to limits in maximum daily intake. To ensure efficacy, 75% of bioactivity had to be released within 30 min at intestinal pH.
We developed a «sprinkle powder», dispersible in juices, yogurts, or milk for easy pediatric use. The lipid-based, anhydrous microspheres had high enzyme load (about 40% w/w) and small size (D90< 120 µm), compatible with easy dispersibility in foods. Measured enzymatic bioactivity was higher than 80 %.
| Property | Parameter | Acceptability Criteria | Experimental |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particles size | D90 (µm) | < 200 µm | < 120 µm |
| Particles shape | Sphericity | Spheroidal | Spherical |
| Yield | % | > 75 | 70-95 |
| Dispersibility in food / beverages | Readily dispersible | Yogurt and juice < 2 min | Dispersible |
| Resistance to Acid media | % activity after 60 min (pH5) | > 90 | 85-93 |
| Fast release | % activity released after 30min | > 75 | 75-85 |
| Target dose | Lipase units (USP) | 2000-4000 | Met criteria |
| Drug load | % weight | > 20% | > 40% |
| Excipients | GRAS/Approved | Met criteria |
Clindamycin Phosphate (topical dermal use)
Acne Vulgaris (AV) is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease, induced by hormonal changes and exacerbated by infective and inflammatory factors. Clindamycin phosphate (CP) is a hydro-soluble antibiotic used alone or in combination with other APIs, like
keratolytic peroxides.
CryoXpand® ability of directly eliminate water during spraying was instrumental for developing a stable, lipid- microencapsulated clindamycin, dispersible in aqueous gel formulations for dermal applications.
We selected lipids combination to embed CP inside the particles (10% load) and reduce drug exposure to keratolytic agents in the aqueous gel. Surface analysis by XPS-ESCA confirmed that CP on particles surface was < 1% of total drug load. Small lipid microparticles could facilitate drug penetration and interaction with skin components once the gel is applied on the affected areas.